
Nature’s Finest: Fruits to Fortify Your Body
In today’s fast-paced world, our lifestyle choices directly impact our health. With increasing demands on our bodies, staying mindful of how we nurture ourselves has never been more crucial. A resilient immune system is the cornerstone of well-being, acting as a shield against infections and helping us thrive.
Who’s at Risk?
Individuals with weakened immunity or underlying health conditions often face greater challenges in staying well. These vulnerabilities highlight the need to prioritize our body’s natural defenses. Fortunately, simple dietary changes can make a significant difference in how effectively we fend off illness.
Understanding the Immune System
The immune system is our body’s built-in security team. It relies on specialized cells—white blood cells, macrophages, and antibodies—to detect and neutralize threats. When this system falters, we’re left exposed to infections, making it essential to keep it in top shape through proper nutrition and care.
Gut Health: The Immunity Hub
Did you know that 85% of our immune system is rooted in the gut? Beneficial bacteria residing there play a starring role in protecting us from disease. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet keeps these microbes thriving, fortifying our defenses naturally and sustainably.
Fruits vs. Supplements
While the market is flooded with immunity-boosting supplements, experts at the Institute for Functional Medicines argue that nature does it better. Brightly colored fruits and vegetables, packed with vitamins and antioxidants, often outshine synthetic options, offering a tastier path to health.
Power-Packed Fruits for Your Plate
Here’s a lineup of accessible, affordable fruits that store well and deliver potent immune support. Each one brings unique nutrients to the table, making them easy additions to your daily routine.
Kiwi: The Tropical Gem
Kiwi, or Chinese gooseberry, is a nutrient-dense superfood with a shaggy exterior and vivid green flesh. Its sweet-tangy flavor is a crowd-pleaser, but its real strength lies in its vitamin C content—93-161 mg per 100 grams, surpassing oranges and lemons. This antioxidant powerhouse fights free radicals and curbs inflammation.
Beyond vitamin C, kiwi offers fiber, folate, carotenoids, potassium, and polyphenols, all collaborating to enhance immunity. Its zinc content also supports respiratory health, making it a go-to for all ages. Toss kiwi slices into salads, infuse them in water, or blend them into smoothies—fresh or frozen works wonders.
Pomegranate: Ancient Healer
Pomegranate’s deep red hue has symbolized vitality since biblical times. Its juice bursts with glucose, amino acids, and vitamin C, complemented by phenols and anthocyanins. These antioxidants boast triple the strength of green tea or red wine, giving your body a robust defense boost.
Flavonoids like quercetin and rutin in pomegranates protect the heart and combat infections, while tannins like punicalagin support respiratory wellness. It’s also a natural ally for managing blood pressure and blood sugar. Pour a glass of pomegranate juice instead of your usual tea or wine.
Oranges: Citrus Champions
Oranges bring a zesty punch of vitamin C, folate, and bioactive compounds to the immune system. Just one orange delivers 92% of your daily vitamin C needs, safeguarding tissues from free radical damage. Their vibrant flavor makes them a refreshing staple.
Oranges also contain polyphenolic flavonoids—hesperidin, naringin, and narirutin—that reduce inflammation and strengthen immunity. Naringin helps regulate blood sugar, adding another layer of benefit. The CDC recommends fresh oranges over processed juices for their superior fiber content.
Banana: Everyday Superstar
Bananas, a globally loved tropical fruit, are both affordable and nutrient-packed. Rich in fiber, carbohydrates, and phytochemicals, they’re a simple yet effective way to fuel your body. Their polyphenolic compounds offer strong antioxidant protection.
Providing 25% of your daily vitamin B-6, bananas support the production of immune cells like cytokines and antibodies. Folate and copper further enhance their immune-boosting profile. Enjoy them fresh, frozen, or baked into treats like banana bread or smoothies.
Pineapple: Tropical Powerhouse
Pineapple’s bright yellow flesh hides a treasure trove of health benefits. Its enzyme, bromelain, aids digestion and fights inflammation, while vitamins C and B-6, plus minerals like manganese and copper, supercharge immunity. It’s a fruit that delivers on taste and function.
Research shows kids who eat pineapple have stronger infection resistance and higher counts of white blood cells like granulocytes. Grill fresh slices, blend frozen chunks into drinks, or snack on bite-sized pieces—pineapple’s versatility shines through.
So there you have it—some amazing fruits to boost your well-being!! Try them out today!
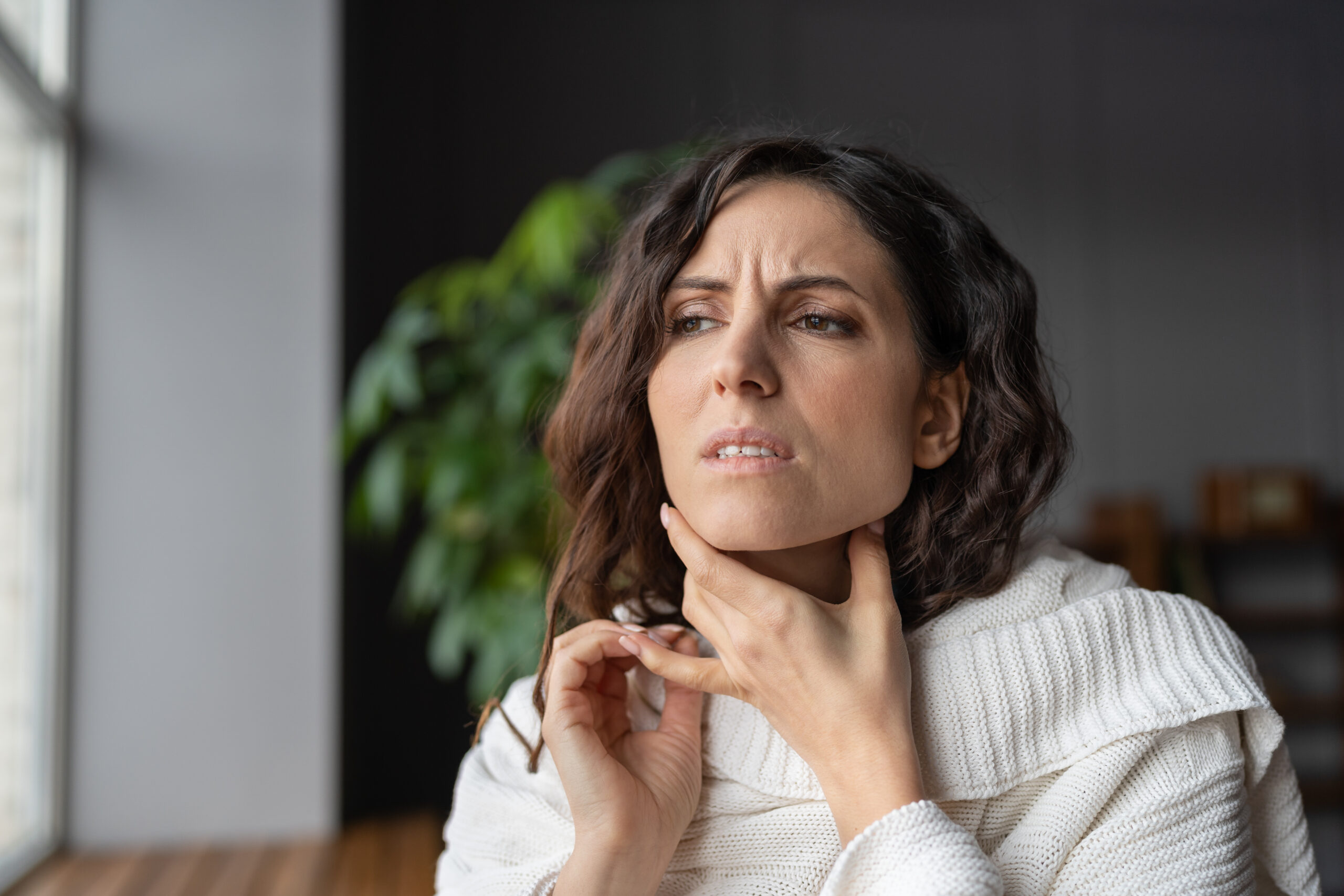

Swollen Glands In The Neck – It’s Not Always Cancer
This is an actual case. Details have been changed slightly to maintain confidentiality.
A 45-year-old lady who was normally fit and well came to my clinic with complaints of small glands that she felt in her neck.
She visited a local general practitioner, who prescribed her a course of antibiotics, but things did not seem to improve. She did not complain of fever or weight loss and was normally active at her job, however, the glands had become painful and she was concerned about them.
On examination, the glands felt quite hard and were only felt on the right side of the neck. Obviously, it was quite concerning to both the patient and myself and hence an ultrasound scan of the neck along with a biopsy of the lymph nodes was performed.
There was a worry that this might either be tuberculosis or some form of cancer. Both of these conditions would impact her job and family life.
After a wait of around three days, the reports finally revealed a condition called Kikuchi disease.
This is a rare condition and was my fifth case in the last 10 years. I thought I would talk about this condition briefly in today’s ‘The Patient Files’ article.
Understanding Kikuchi Disease
Kikuchi disease, also known as Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease or histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis, is a rare but benign condition. It primarily affects the lymph nodes, which are small glands that play a crucial role in the immune system by filtering harmful substances and fighting infections.
Who Does It Affect?
Kikuchi disease most commonly affects young adults, particularly women under the age of 40. Although it can occur in people of all ages and genders, it is less common in older adults and young children. The disease is found worldwide but appears more frequently in people of Asian descent.
How Does It Occur?
The exact cause of Kikuchi disease is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an abnormal immune response. Given that it frequently follows a flu-like illness, some researchers think viral infections might be the cause. However, no specific virus has been definitively linked to the condition.
Clinical Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of Kikuchi disease can vary but often include:
Swollen lymph nodes: Usually in the neck, these nodes can become tender and painful. It is seen in 100% of cases. The glands vary between 0.5 to 4 cm.
Fever: Many patients (around 30–50%) experience a mild to moderate fever. It usually lasts for a week, but some patients have reported fevers lasting up to a month.
Fatigue: General tiredness and weakness are frequently reported.
Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur in some cases.
Rash: Occasionally, a skin rash may develop.
These symptoms can last from a few weeks to several months and typically resolve on their own.
Rare cases may present as neurological symptoms. Aseptic meningitis, which is inflammation of the lining of the brain, is the most common neurological complication.
There are some cases of association with COVID-19.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Kikuchi disease can be challenging because its symptoms are similar to those of other conditions, such as infections,, tuberculosis, lymphoma (a type of cancer), or autoimmune diseases like lupus.
A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Some of the commonly performed tests include:
Lymph node biopsy: The definitive diagnosis is made through a biopsy of the affected lymph node. A small sample of tissue is examined under a microscope to look for characteristic signs of the disease.
Blood tests: While blood tests are not specific for Kikuchi disease, they can help rule out other conditions.
Imaging studies: Ultrasound or CT scans may be used to evaluate the extent of lymph node involvement. This is usually unnecessary
Treatment Options
There is no specific treatment for Kikuchi disease, as it often resolves on its own over 3 to 4 months. However, supportive care can help manage symptoms.
Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and fever.
Rest and hydration: Adequate rest and fluids are essential for recovery.
Corticosteroids: In more severe cases, doctors might prescribe steroids to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery.
Most people recover fully without long-term complications. However, a small number of cases may develop Systemic Lupus Erythematosus years later. Regular follow-up with a doctor is important to monitor progress and ensure that symptoms are improving.
Conclusion
Kikuchi disease, while rare, is a condition that primarily affects young adults and manifests through swollen lymph nodes, fever, and other flu-like symptoms.
Though its exact cause is unknown, it is generally self-limiting and responds well to supportive care. If you suspect you have symptoms of Kikuchi disease, it is crucial to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Healthcare Advancements in India: A Decade of Progress and Future Prospects
India has witnessed significant advancements in its healthcare sector over the last decade, transforming the landscape of medical services and improving the well-being of its population. A combination of technological innovations, policy reforms, increased investments, and enhanced accessibility has paved the way for a remarkable healthcare revolution. This essay explores the key developments in Indian healthcare over the past ten years and highlights the potential future advancements that lie ahead.
Healthcare Advances in India: The Last Decade
Technological Innovations
The last decade witnessed a rapid integration of technology into the Indian healthcare system. Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telemedicine, mobile health applications, and digital diagnostics have gained significant momentum.
These advancements have enhanced patient care, facilitated remote consultations, enabled efficient health data management, and increased access to healthcare services in remote areas.
Infrastructure Development
India has witnessed substantial growth in healthcare infrastructure, including the establishment of new hospitals, medical colleges, and research institutions. The expansion of healthcare facilities, especially in rural areas, has improved accessibility and reduced the burden on urban centers.
Additionally, the growth of specialized centers, such as cancer institutes and cardiac hospitals, has improved disease-specific care.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has implemented several healthcare initiatives to promote affordable and accessible healthcare. The National Health Mission (NHM), Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), and National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) are notable examples.
These initiatives focus on providing healthcare services to the underserved population, reducing out-of-pocket expenses, and integrating digital health infrastructure.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Advancements
India has emerged as a global hub for pharmaceutical manufacturing and research. The last decade witnessed significant growth in the developing of generic drugs, biosimilars, and the establishment of research and development centers.
These advancements have improved the availability and affordability of essential medicines, benefiting both the domestic and international populations.
Awareness and Prevention
With a focus on preventive healthcare, there has been a notable increase in health awareness campaigns and initiatives promoting healthy lifestyles. Public health programs have addressed critical issues such as vaccination drives, maternal and child health, and non-communicable disease prevention.
The emphasis on preventive measures has helped reduce the disease burden and improve overall population health.
Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics
The coming decade holds immense potential for the integration of AI and data analytics in healthcare. Machine learning algorithms can aid in early disease diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics for epidemics.
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can enhance patient engagement and streamline healthcare delivery.
Precision Medicine
Advancements in genomics and molecular diagnostics will pave the way for precision medicine in India. Tailoring treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup and lifestyle factors can optimize therapeutic outcomes and reduce adverse effects.
Precision medicine holds promise in tackling complex diseases such as cancer and rare genetic disorders.
Health Insurance Reforms
Efforts to strengthen health insurance coverage and increase awareness about health insurance schemes are expected to continue. Expanding the scope of coverage, reducing exclusions, and improving reimbursement mechanisms will enhance financial protection for individuals and reduce the financial burden of healthcare expenses.
Digital Health Transformation
The ongoing digitization of healthcare services will accelerate in the coming decade. The National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) aims to create a unified digital health ecosystem, including digital health records, e-pharmacies, and telemedicine platforms.
This transformation will improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery, enhance data interoperability, and empower patients to take control of their health.
Conclusion
The last decade has witnessed remarkable advancements in India’s healthcare sector, driven by technological innovations, policy reforms, and increased investments. Improved accessibility, infrastructure development, and focus on preventive healthcare have resulted in significant progress.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI, precision medicine, and digital health transformation holds tremendous potential for further advancements in India’s healthcare system. By leveraging these opportunities, India can strive towards achieving universal healthcare, reducing health disparities, and improving the overall well-being of its population.
Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Inhibitors in Heart Failure Management
The Heart Failure Journal of India published an article titled ‘Worsening heart failure and current management strategies with a focus on soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators‘. Here is a brief summary of this article.
This paper is a review article that discusses the current management strategies for worsening heart failure (WHF), with a focus on soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators.
The authors begin by defining WHF as a critical point in the disease trajectory of heart failure (HF) patients that significantly affects prognosis negatively.
They then discuss the pathophysiology of WHF, which involves neurohormonal activation, inflammation, and oxidative stress. The authors go on to describe the current standard of care for WHF, which includes diuretics, vasodilators, and inotropic agents.
However, they note that these therapies have limitations and can be associated with adverse effects.
They then introduce sGC stimulators as a potential new class of drugs for WHF management. sGC is an enzyme that plays a key role in regulating vascular tone and cardiac function.
sGC stimulators are drugs that enhance the activity of sGC by binding to its heme moiety and increasing cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels. This leads to vasodilation, anti-inflammatory effects, and improved cardiac function. The authors review several clinical trials that have investigated the efficacy and safety of sGC stimulators in HF patients.
They note that these trials have shown promising results in terms of improving symptoms, exercise capacity, and quality of life. Additionally, sGC stimulators have been shown to have favorable hemodynamic effects and to reduce biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress.
The authors also discuss some potential limitations of sGC stimulators, such as their cost and the need for further long-term safety data. They note that ongoing clinical trials will provide more information about the efficacy and safety of these drugs. Overall, the authors conclude that sGC stimulators represent a promising new class of drugs for WHF management.
They suggest that future research should focus on identifying patient subgroups who may benefit most from these drugs and on investigating their long-term safety and cost-effectiveness. In summary, this review article provides an overview of the current management strategies for worsening heart failure and introduces sGC stimulators as a potential new class of drugs for this condition.
The authors review several clinical trials that have investigated the efficacy and safety of sGC stimulators in HF patients and conclude that these drugs represent a promising new treatment option.
You can click here to read the article.
Reference
Talha KM, Greene SJ, Chopra VK, Butler J. Worsening heart failure and current management strategies with a focus on soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators. Heart Failure journal of India 2023;1:5-11.
Heart Failure Patient Guide By Dr Vivek Baliga
Heart failure is a chronic condition characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood effectively, leading to insufficient oxygen and nutrients reaching the body’s tissues. This condition affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and long-term prognosis is crucial for managing heart failure effectively.
Heart failure can be classified into two types: systolic heart failure and diastolic heart failure. Systolic heart failure occurs when the heart muscles are weakened and cannot contract with enough force to pump blood adequately. Diastolic heart failure, on the other hand, happens when the heart muscles become stiff and cannot relax properly, leading to impaired filling of the heart chambers. Both types result in decreased cardiac output and fluid buildup in the lungs and other body tissues.
Several factors can contribute to the development of heart failure. The most common causes include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, previous heart attacks, heart valve problems, and certain conditions that weaken the heart muscles, such as cardiomyopathy and myocarditis. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, smoking, and a family history of heart disease.
The treatment of heart failure aims to relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve the patient’s overall well-being. Medications play a crucial role in managing the condition. Diuretics are commonly prescribed to reduce fluid retention, while ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers help improve heart function, lower blood pressure, and reduce the workload on the heart. Additional medications like aldosterone antagonists and digoxin may be used in specific cases.
Lifestyle modifications are also vital in managing heart failure. These include adopting a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats, engaging in regular exercise within recommended limits, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption. Patients with severe heart failure may require medical devices like pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), or left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) to support heart function.
Despite advances in treatment, heart failure is a chronic condition that often requires lifelong management. The long-term prognosis can vary depending on various factors, including the underlying cause, the patient’s overall health, and the severity of the condition. Early diagnosis, adherence to treatment, and regular follow-up care are crucial in improving outcomes and prolonging survival.
While heart failure is a progressive condition, advances in medical therapies and interventions have significantly improved the prognosis for many patients. However, it is important to note that heart failure is a serious condition that can lead to complications, such as arrhythmias, kidney problems, and fluid buildup in the lungs. Close monitoring, medication adjustments, and lifestyle modifications are essential to manage symptoms, prevent exacerbations, and improve long-term outcomes.
In conclusion, heart failure is a chronic condition characterized by the heart’s inability to effectively pump blood, resulting in inadequate oxygen and nutrients reaching the body’s tissues. It can be caused by various factors, including coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and heart muscle abnormalities. Treatment involves medication, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, medical devices. While heart failure requires lifelong management, early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and regular follow-up care can significantly improve the long-term prognosis and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
To read my full guide to heart failure, click here.

From Spice Rack to Medicine Cabinet: Immune-Boosting Spices and Herbs
Spices and herbs have been used for centuries in culinary and medicinal practices. These natural ingredients are packed with potent antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties that can help support overall health and wellness. From the spice rack to the medicine cabinet, here are some immune-boosting spices and herbs that you should consider adding to your diet.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a spice that has been used for centuries in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties. The active ingredient in turmeric, curcumin, has been shown to have immune-boosting effects by modulating the activity of immune cells. In addition to its immune-boosting properties, turmeric is also known for its ability to support brain health, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation.
Ginger
Ginger is a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant that has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments. Gingerol, the active compound in ginger, has been shown to have immune-boosting properties by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and viruses. Additionally, ginger has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and relieving pain.
Garlic
Garlic is a member of the onion family and has been used for thousands of years for its medicinal properties. Garlic contains allicin, a sulfur compound that has been shown to have immune-boosting properties by stimulating the production of white blood cells. Garlic is also known for its ability to lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and fight off infections.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a popular spice that has been used for centuries in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties. Cinnamon contains powerful antioxidants that can help protect the body from oxidative damage. Additionally, cinnamon has been shown to have immune-boosting effects by improving the activity of immune cells and reducing inflammation.
Echinacea
Echinacea is an herb that has been used for centuries by Native Americans for its immune-boosting properties. Echinacea contains compounds that have been shown to stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections. Additionally, echinacea has been shown to reduce the severity and duration of cold and flu symptoms.
Elderberry
Elderberry is an herb that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its immune-boosting properties. Elderberry contains compounds that have been shown to reduce inflammation and stimulate the production of cytokines, which are essential for immune function. Additionally, elderberry has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity and duration of cold and flu symptoms.
Astragalus
Astragalus is an herb that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries for its immune-boosting properties. Astragalus contains compounds that have been shown to stimulate the production of white blood cells and increase the activity of immune cells. Additionally, astragalus has been shown to be effective in reducing the severity and duration of cold and flu symptoms.
Oregano
Oregano is a spice that is commonly used in Mediterranean cuisine and has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Oregano contains compounds that have been shown to have antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties. Additionally, oregano has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and fighting off infections.
Licorice Root
Licorice root is an herb that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its immune-boosting properties. Licorice root contains compounds that have been shown to stimulate the production of white blood cells and increase the activity of immune cells. Additionally, licorice root has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and fighting off infections.
Holy Basil
Holy basil is an herb that has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for thousands of years for its immune-boosting properties. Holy basil contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties. Additionally, holy basil has been shown to be effective in reducing stress, improving mood, and promoting overall well-being.
Rosemary
Rosemary is a spice that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Rosemary contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Additionally, rosemary has been shown to improve digestion, reduce stress, and improve cognitive function.
Thyme
Thyme is a herb that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Thyme contains compounds that have been shown to have antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties. Additionally, thyme has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and fighting off infections.
Sage
Sage is a spice that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Sage contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Additionally, sage has been shown to improve cognitive function, reduce inflammation, and improve digestion.
Black Seed
Black seed, also known as black cumin, is a spice that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Black seed contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties. Additionally, black seed has been shown to be effective in reducing blood sugar levels, improving heart health, and fighting off infections.
Peppermint
Peppermint is a herb that has been used for centuries for its medicinal properties. Peppermint contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. Additionally, peppermint has been shown to improve digestion, reduce stress, and relieve headaches.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, incorporating immune-boosting spices and herbs into your diet can provide numerous health benefits. These natural ingredients are packed with potent antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties that can help support overall health and wellness.
However, it is important to note that these herbs and spices should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If you are experiencing any health concerns, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.

Simple Ways To Strengthen Your Knee
Strengthening the knee joint and keeping it that way is crucial for a healthy lifestyle. The capacity to walk, run, and leap depends on the health of the knee joint because of the support and stability it provides for the rest of the body.
Yet, knee discomfort and pain can develop with age or after an injury.
I had spoken about some ways to increase the strength of the knee joint on my health blog HeartSense.
To avoid this, consider the following six methods for bolstering your kneecap’s stability and strength.
Maintain Your Weight
Keep your weight where it should be; extra kilos place extra stress on your knees, which can cause injury and discomfort.
By keeping your weight where it should be, you can reduce pressure on the joint and boost its durability. Maintaining a healthy weight can be accomplished by eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, complete grains, and lean protein.
Exercise Daily
Regular exercise is essential for keeping the knee joint strong. Cycling, swimming, and yoga are examples of low-impact exercises that can aid with joint flexibility and mobility.
Joint strength can also be increased by working the muscles around the knee, specifically the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves.
Hydrate Well
Maintaining healthy joints requires a commitment to adequate hydration. As a result, the likelihood of damage to the cartilage in the knee is decreased.
Eat Foods Rich In Calcium
Bone and joint health can be maintained in part by eating foods high in calcium and vitamin D.
Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals are all good sources of calcium, and fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified meals are all good sources of vitamin D.
Here are some fantastic sources of calcium in your diet.
Wear The Right Footwear
To lessen the force exerted on the knee joint during exercise, use shoes with appropriate arch support. Try to find some shoes with a good amount of padding and arch support.
Take A Break
Reducing strain on the knee joint during physical activity is as simple as taking a rest every so often. Don’t overwork the joint by doing the same thing repeatedly without taking breaks to stretch and relax.
Exercises To Strengthen The Knee Joint
Let’s discuss ways to strengthen the knee joint through exercise.
Squats: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and lower your body down as if you’re sitting in a chair. Keep your knees behind your toes and your back straight. Hold the position for a few seconds and then slowly rise back up. Repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
Step-ups: Find a step or platform that’s around knee height. Step onto it with one foot and then step back down. Repeat 10-15 repetitions on one leg before switching to the other.
Lunges: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and take a large step forward with one leg. Lower your body down until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Hold the position for a few seconds and then rise back up. Repeat 10-15 repetitions on one leg before switching to the other.
Leg curls: Lie face down on a mat with your legs straight out behind you. Slowly bend one leg and lift your heel towards your buttocks, keeping the other leg straight. Hold the position for a few seconds and then slowly lower your leg back down. Repeat 10-15 repetitions on one leg before switching to the other.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, a strong knee joint is essential for an active and healthy lifestyle.
Joint health can be enhanced through a combination of a healthy diet, frequent exercise, and effective weight management.
Joint strength can also be increased by doing workouts that target the muscles close to the knee. Never begin a new workout program without first talking to your doctor.

Lemons – 7 Amazing Health Benefits
Lemons are a popular part of many diets because they are good for your health in many ways. Here are seven ways that lemons might be good for your health, with a little more information:
Boosts Immune System
Lemons are a great source of vitamin C, which helps the immune system by making white blood cells. Getting enough vitamin C can also shorten the length and severity of colds and flu.
Helps Digestion
Lemon juice can help digestion by stimulating the production of digestive juices and promoting healthy bowel movements. This can help digestion and keep you from getting constipated.
Helps In Dieting
The soluble fiber pectin in lemons can help reduce hunger and make you feel full, which makes it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet and lose weight.
Reducing inflammation
Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in lemon juice can help reduce inflammation in the body, which could lower the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Protects The Skin
Vitamin C and other antioxidants in lemons can help protect the skin from the harmful effects of free radicals, which can cause premature aging and damage to the skin.
Lowers Cancer Risk
Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in lemons may help lower the risk of certain types of cancer, such as breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer. But more research needs to be done to confirm these results.
Reduces Cholesterol
Flavonoids, which are found in lemons, may help lower cholesterol and lower the risk of getting heart disease. As part of a healthy diet, drinking lemon water or eating more citrus fruits may help improve heart health.
Lipoma – Frequently Asked Questions
Many of my patients have small swellings on various parts of the body. This is a fat deposit called lipoma.
Here are some of the frequently asked questions about lipomas.
What Is A Lipoma?
A lipoma is a small collection of fat tissue within an outer capsule. It is considered a fat tumor, but a benign one.
Think of it to look like an egg yolk.
How Common Is A Lipoma?
They are fairly common and are often seen in men.
Studies have found that 1 in a 1000 people will have a lipoma at some point in their lifetime.
There are small role of genetics in the development of lipomas. Around 2 – 3% of cases run in families.
Though seen in younger patients as well, most cases are evident between the ages of 40 – 60 years of age.
Where Are Lipomas Seen Commonly?
The most common site of lipoma is the chest and back. In practice, I see a lot of patients with lipoma on their arms, as shown in the picture.
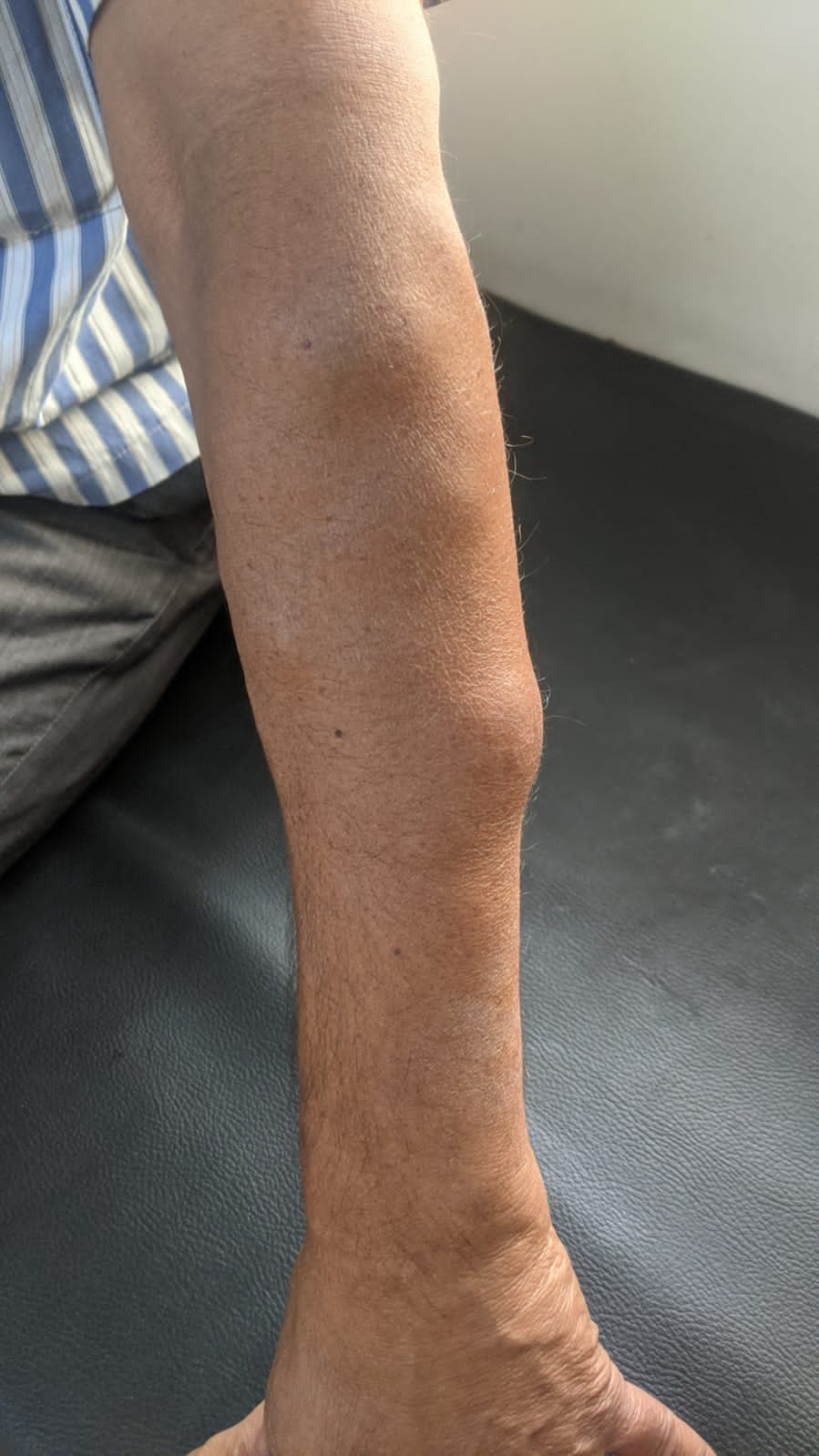
There are not the only places lipomas are seen. They may be even seen in the gastrointestinal tract, heart and almost any other organ of the body.
Is Lipoma A Cancer?
Fortunately, a lipoma is a benign tumor. It is not a cancer.
Is Lipoma Hereditary?
As mentioned earlier, there are some cases where it can be passed on through generations. This is very rare though, and has to do with mutations in certain genes.
How Big Can Lipomas Grow?
Most lipomas measure between 1 – 2 cm. Giant lipomas have been seen, and can measure over 10 cm.
Symptoms And Signs Of Lipoma
As such, lipomas are a cosmetic issue and rarely cause any symptoms when they are on the skin.
If they are located within the organs, then they can cause symptoms in rare cases.
For example, if a lipoma is present in the digestive tract, it can cause obstruction. The persons may be unable to pass stools.
Patients with a lipoma in the lung tissue may have a cough or breathing difficulty.
They may also be present in the heart, muscles, bones and nerves as well.
Diagnosis Of Lipoma
A clinical diagnosis is often sufficient for lipomas on the skin. An ultrasound scan can help confirm this.
In patients where lipomas are hidden within the body, further tests such as CT scans or MRI scan can help.
How Are Lipomas Treated?
Most people accept lipomas as a part of life and do not bother with any treatment.
Some wish to get it removed surgically, especially if they are cosmetically unpleasant.
Removal should be done by an expert surgeon, taking care to remove the fat tissue and the capsule that surrounds it. It incompletely removed, it could lead to a recurrence of the tumor.
If my patients wish to get them removed, I usually send them to a plastic surgeon who can remove them with minimal scar formation after wound healing.
What Is The Prognosis Of Lipomas?
They have an excellent prognosis. They are rarely life-threatening, unless they occur in rare areas.
Skin Abscess – A Patient Guide
Often in clinical practice, I encounter patients who have developed skin infections. Sometimes the skin infection can be serious enough to require admission to the hospital.
These infections that require admission usually ends up being skin abscess.
What Is A Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess is essentially an infection of the skin where there is space accumulated under the skin. It is very similar to a pimple but is significantly larger and is seen deeper under the skin.
Where Are Skin Abscesses Usually Seen?
The most common site of skin abscess development is the groin, armpits, buttocks, and extremities.
However, I have seen patients develop abscesses on the scalp and on the back as well.
Symptoms And Signs
In mild cases, skin abscesses will just be a collection of pus with some redness of the skin surrounding it. It can be painful when pressed and can be warm to the touch.
In severe cases, the skin abscess can spread rapidly from the original area and affect a large area around it. This can become extremely painful and can lead to fever and severe fatigue.
I recently treated a patient who had a skin abscess of the inner thigh and who came to the clinic with severe giddiness and low blood pressure. This is because the infection had spread to the bloodstream and was affecting the normal working physiology of the body.
If the skin abscess spreads to nearby areas it can lead to a condition called cellulitis, which I shall discuss in a separate article.
Who Develops A Skin Abscess? Risk Factors.
Skin abscesses can develop in literally anyone. However, they tend to be more serious in patients who have a history of type 2 diabetes and those who do not maintain adequate hygiene.
What Causes A Skin Abscess?
Skin abscesses are caused by bacteria. The most common bacteria that cause infection are Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus.
Investigations
It is easy to diagnose an abscess through clinical examination alone. They range between 1 to 3 cm in size but may become larger as I have discussed above.
Sometimes on the surface, they have a tiny yellow spot which is the pus that is trying to come out.
Patients who have a skin abscess require a blood test that will help determine the presence of infection within the bloodstream. Those who have diabetes will require a blood sugar test as well.
In some patients, an ultrasound scan or a CT scan may be required to determine the depth and true size of the abscess.
If pus starts to come out of the skin abscess, then a wound swab will be sent out to the lab for analysis.
Treatment Of Skin Abscess
The primary treatment for managing skin abscesses is incision and drainage i.e. a surgical procedure. A small abscess can dissolve with simple antibiotics and warm compression.
Larger abscesses can be difficult to treat as an outpatient and are best managed in a hospital setting.
Intravenous antibiotics will be administered to the patient and once the abscess has ‘calmed down‘ then the surgical procedure will likely be needed.
The surgical procedure is called incision and drainage. The surgeon, under anesthesia, will make a small cut on the top of the abscess to allow the pus to come out.
Once the pus comes out, the surgeon will insert their gloved index finger or a device to clean out all the bus from within the abscess cavity. Addressing will be and then applied to allow any remaining bus to get soaked into the dressing.
After discharge, patients may require ongoing antibiotic treatment along with regular dressings.
Complications
If an abscess is left untreated then it can spread rapidly and make the patient seriously ill. It is always best to seek advice early so that simple treatments can help resolve the condition completely.
